Examining Different Types of Flowmeters
 Engineers and facility managers looking for an air or gas flow measurement solution walk into the flow meter comparison and selection process with so many different types of flow meters that it can be difficult to narrow down the choices to the most effective technology for their application.
Engineers and facility managers looking for an air or gas flow measurement solution walk into the flow meter comparison and selection process with so many different types of flow meters that it can be difficult to narrow down the choices to the most effective technology for their application.
Primarily, there are two main categories: volumetric flow technologies and thermal mass flow technologies. Within these two categories are different types of flow meters functioning on various different flow measurement principles.
Quickly jump to the content that’s relevant to you:
Choosing the Best Flow Meters for Industrial Gas Applications
When looking at a flow meter comparison, it is important to understand what makes different types of flow meters unique and the features that are most important for your needs. There are a few key characteristics to consider when choosing the best flow meters for industrial gas applications.
Gas Type
One of the first factors to think about in a flow meter comparison is the type of gas flowing in the pipes. Some flow meters are versatile enough to work with both clean and dirty gases. Others, particularly those with moving parts, can only be used in clean gas applications. Knowing which type of gas is flowing through your pipes can eliminate a few different types of flow meters early on.
Temperature or Pressure Compensation
Temperature and pressure can greatly impact gas flowing through pipes, leading to inaccurate readings from a flow meter. If these outside factors are a concern in your application, a flow meter that does not require compensation for temperature or pressure is a better choice that will make the process easier.
Pressure Drop
Pressure drop is another factor that may be important for your application. Pressure drop occurs when the pressure of the gas exiting the pipe is less than the pressure of the gas entering the pipe. Some flow meters offer low pressure drops, while others can lead to a significant decrease in pressure. These drops could be a deciding issue, depending on your application.
Cost
Your budget is key when selecting the best flow meters for industrial gas applications. Some flow meters, such as ultrasonic flow meters, can be a significant initial purchase, while other options are relatively inexpensive up front but may require more maintenance costs down the road. Consider both short-term and long-term expenses when choosing between different types of flow meters.
Maintenance
When selecting a flow meter, consider the ongoing calibration and repair costs of your choice. Remember that more moving parts and mechanical components needed for a flow meter to operate result in more frequent maintenance needs.
Pipe Size
Some flow meters work with a wide range of different pipe sizes, but others may be very limited. Figuring out the pipe size for your application early on may also eliminate a number of different types of flow meters in your flow meter comparison.
Rangeability
Rangeability refers to the minimum and maximum level at which a flow meter can measure a gas. This is an important consideration if you require a flow meter that can measure both small and large flows. A flow meter having wide rangeability is a solid feature for most applications.
Exploration of Available Technologies and Flow Measurement Principles for Gas Flow Measurement
The next part of our flow meter comparison will discuss the basic aspects of these technologies to help guide you toward the right technology for your industrial gas flow measurement application. Below is a list of the most commonly used technologies in industrial markets:
Thermal Flow Meters
Thermal mass flow meters utilize the thermal sensing principle by using a constant temperature differential to measure the mass flow rate of air and gases. These meters typically feature temperature sensors and electric heaters.
Thermal flow meters are a great option for a wide range of applications, and they work well for both clean and dirty gases. Since they have no moving parts, thermal flow meters are easier and less expensive to maintain than many alternatives. They also feature low pressure drops and wide rangeability. They can be used with a variety of pipe sizes, making them the leader among the best flow meters for industrial gas applications.
Thermal flow meters are very good at the following:
-
Suitable gas application: Clean and dirty gases
-
Mass flow measurement: No need to temperature or pressure compensation
-
Pressure drop: Low
-
Cost effective
-
No moving parts
-
Pipe size options: Wide range of pipe sizes
-
Rangeability: 100:1

Turbine Flow Meters
Turbine meters use the mechanical action of a rotor spinning in obstruction to the flow to measure the volumetric flow in the pipe. A turbine flow meter is able to measure gas flow based on the speed at which the flow rotates the rotor’s blades.
These meters are very accurate and can be used with a range of different pipe sizes but are limited to clean gas applications. Turbine flow meters also exhibit high pressure drop, and the moving parts needed for their operation may require more frequent maintenance. Lastly, turbine flow meters may not be accurate when the pipes are exposed to temperature or pressure changes, making compensation for those necessary.
This type of flow meter is good at the following:
Characteristics that could be better:
-
Relative cost: Medium
-
Rangeability: 20:1
Turbine flow meters are not advisable when it comes to:
-
Suitable gas applications: Clean gases only
-
Volumetric flow measurement: May require temperature or pressure compensation to calculate mass flow
-
Pressure drop: High
-
Uses a rotor: Moving parts may increase maintenance costs

Vortex Shedding Meters
Vortex flow meters place an obstruction in the path of the gas flow to create a swirling of the gas. The pressure variations caused by the swirling effect are measured by a sensor(s) placed after the obstruction.
A vortex shedding meter works for both clean and dirty gases, and with a range of pipe sizes. It is important to note that the mechanical sensors used in vortex shedding meters may require frequent maintenance and recalibrations to remain accurate. These meters will also require compensation for temperature and pressure in many applications and only work well with very high flow rates.
This type of flow meter is good at the following:
Characteristics that could be better:
-
Pressure drop: Medium
-
Relative cost: Medium
-
Rangeability: 10:1
Vortex shedding meters are not advisable when it comes to:

Coriolis Flow Meters
When flow is present in the tubes of the Coriolis flow meter, it causes a twist in the tube(s). Pick off coils and magnets measure the twisting effect. The Delta T and time leg is directly proportional to the mass flowing through the tubes.
Coriolis flow meters can be used with both clean and dirty gases and feature low pressure drops. They also do not require temperature or pressure compensation and have no moving parts that increase maintenance needs. On the downside, these meters are limited in the range of pipe sizes they can work with.
Although they often require less maintenance than some alternatives, a flow meter comparison looking at cost will show that Coriolis flow meters are generally a bigger initial expense.
This type of flow meter is good at the following:
Characteristics that could be better:
Coriolis flow meters are not advisable when it comes to:

Differential Pressure (Orifice) Flow Meters
The most common differential pressure (DP) flow meter is the orifice plate. This device is used to measure flow rate by measuring pressure before and after the orifice plate placed in the pipe.
Flow rate must be calculated using published formulae.
Orifice flow meters work well for both clean and dirty gases. They are also relatively low in cost and have no moving parts to maintain. Orifice flow meters do require compensations for temperature and pressure, however, and may require additional sensors to give accurate readings. They also demonstrate high pressure drop and have very limited rangeability compared to different types of flow meters.
This type of flow meter is good at the following:
Orifice flow meters are not advisable when it comes to:

Positive Displacement Flow Meters
Positive Displacement (PD) flow meters use gears or pistons to divide the flow into fixed metered volumes. The timing of the metered volumes determines the volumetric flow rate.
These meters are limited to clean gas applications, but do work with a wide range of pipe sizes. The gears or pistons that allow PD flow meters to work may be difficult to maintain, however, and these meters are often an expensive option. PD flow meters also exhibit high pressure drop, and you will need to compensate for temperature and pressure in many applications.
This type of flow meter is good at the following:
Characteristics that could be better:
Positive Displacement flow meters are not advisable when it comes to:
-
Suitable gas applications: Clean gases only
-
Volumetric flow measurement: May require temperature or pressure compensation to calculate mass flow
-
Pressure drop: High
-
Relative cost: High
-
Uses gears or pistons: Moving parts may increase maintenance costs

Ultrasonic Flow Meters
Ultrasonic flow meters emit ultrasound pulses along and against the path of flow in the pipe. Using either transit time or doppler effect, these flow meters calculate the volumetric flow rate.
An ultrasonic flow meter works wells for both clean and dirty gases, and features low pressure drop. It also works with many pipe sizes, and its lack of moving parts makes it easier to maintain. These meters can be some of the most expensive among different types of flow meters, however, and may still require temperature or pressure compensation for many applications.
This type of flow meter is good at the following:
Characteristics that could be better:
Ultrasonic flow meters are not advisable when it comes to:

The Case for Fox’s Thermal Mass Flow Meters
For customers searching for a lower cost, higher accuracy, low flow measurement meter, thermal mass flow meters for gas by Fox Thermal beat DP meters and the other flow technologies on the market today.
Compare the model FT4X thermal mass flow meter equipped with the state-of-the-art DDC-Sensor™ technology, new expanded Gas-SelectX® gas selection menu, CAL-V™ Calibration Validation, and a standard data logger with date and time stamp as the thermal flow meter alternative to other technologies.
Look at the other benefits thermal gas flow meters offer over other flow measurement technologies:
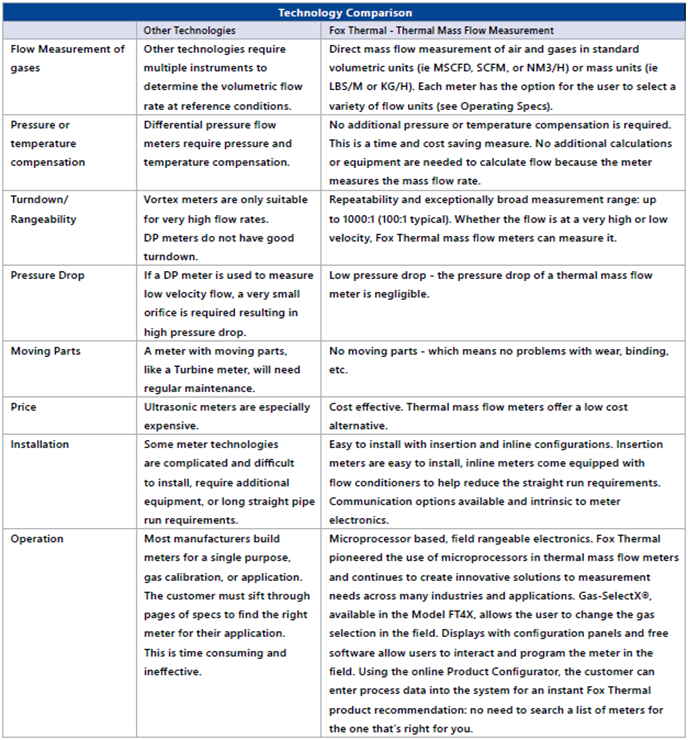
Looking at the flow meter comparison above, it is clear that Fox’s thermal mass flow meters have a clear advantage over other technologies. Fox’s thermal mass flow meters are the best flow meters for industrial gas applications and have substantial benefits over different types of flow meters for a wide range of needs and requirements.
See What Flow Meter Works Better According to Your Needs >>














