 Biogas
Biogas

Contact Sales Fox Thermal
Fill out the form below to contact a Fox Thermal Representative.
Need to talk to someone immediately, give us a call, 831-384-4300.
Account Logout
Are you sure you want to log out?

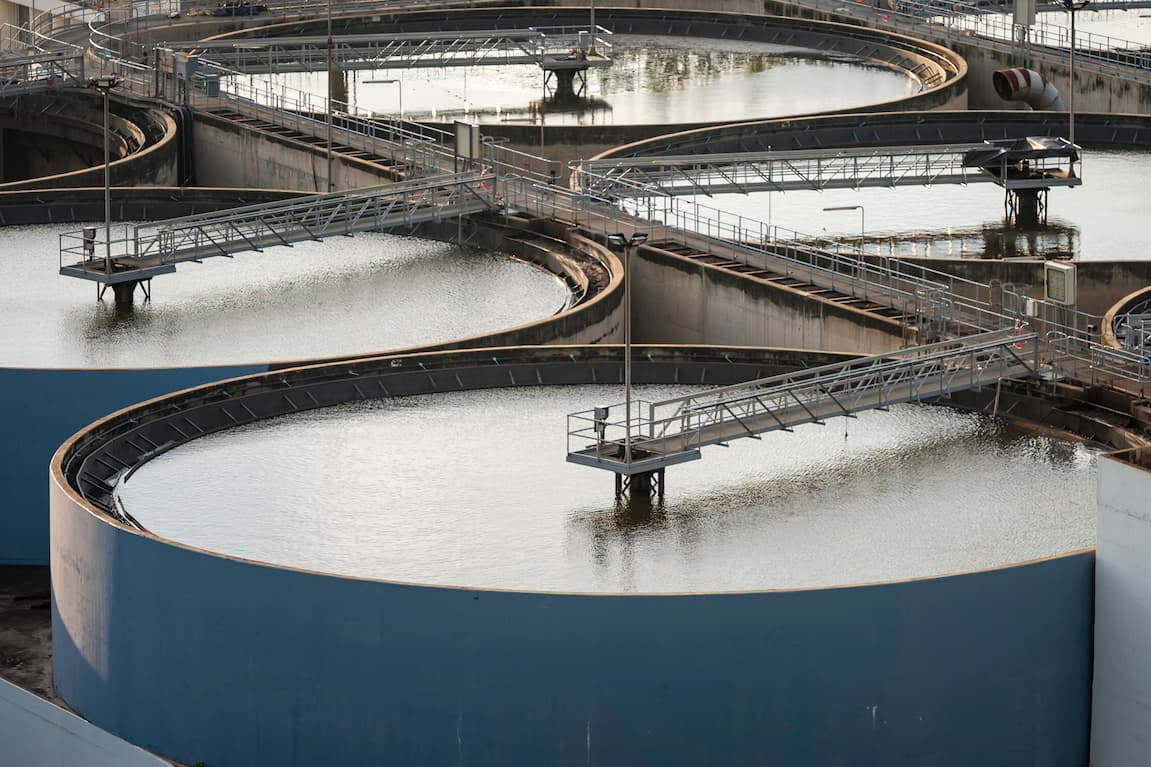
Gas flow meters are essential tools for managing aerobic and anaerobic processes at wastewater treatment plants. Thermal mass type flow meters from Fox Thermal are the ideal solution for measuring gas flow rates, reducing costs, and meeting emissions requirements for greenhouse gases.

Thermal mass flow meters require no additional pressure or temperature compensation instrumentation and unlike PD or turbine meters, they have no moving parts that can wear or bind so they require no maintenance.
Anaerobic wastewater digesters produce biogas mixtures that can change over time. To reprogram the percentages of component gases in your flow meter and avoid sending it back to the factory for recalibration, you need a more flexible solution.
Compared to DP meters, Fox Thermal mass flow meters provide a large turndown rate, with a repeatability of up to 1,000:1 (typically 100:1) for very high velocity or for very low flow rates, which are common in anaerobic digesters.
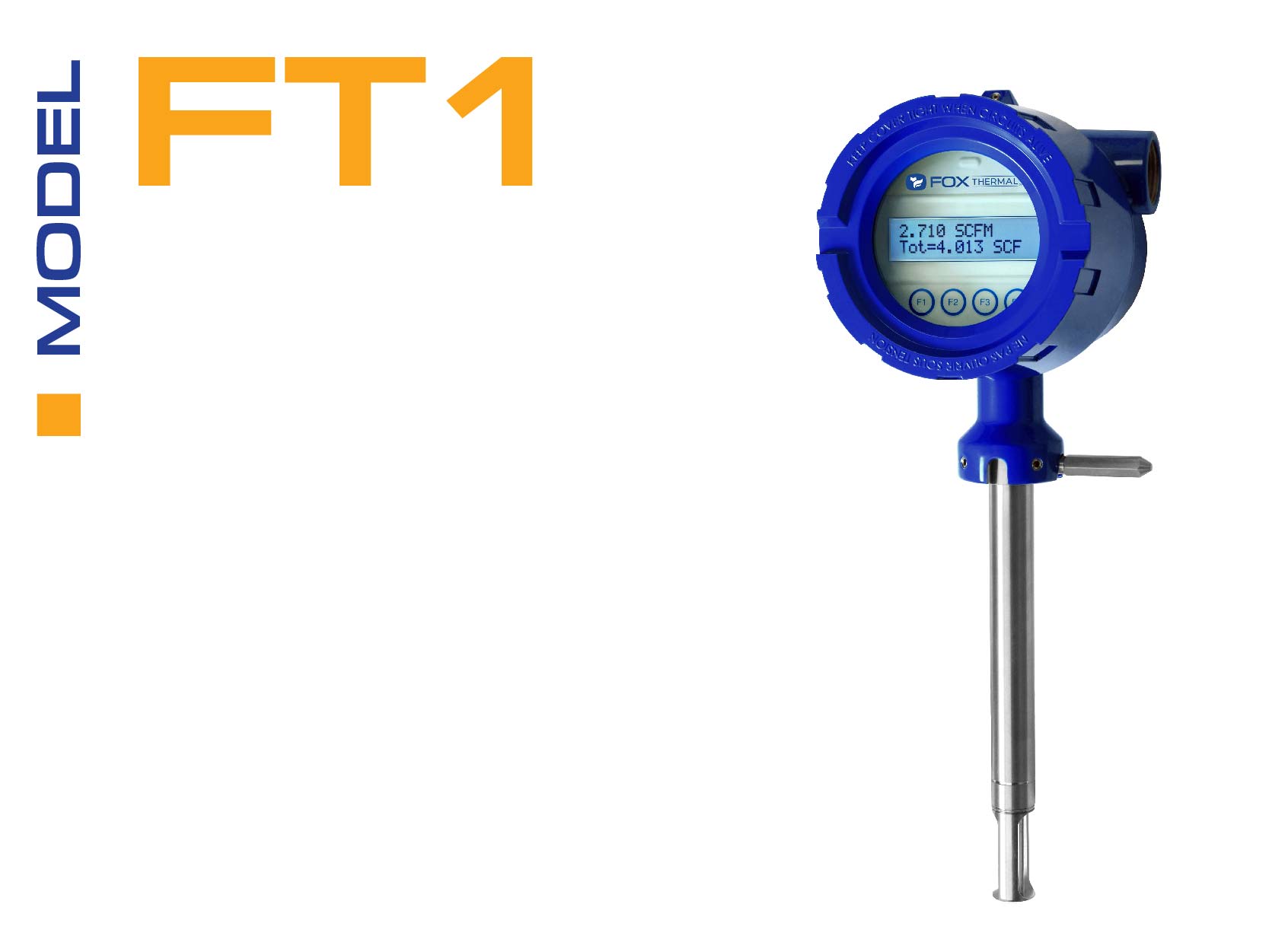

The FT1 is the most popular flow meter for wastewater air and gas applications. Features include a list of pure gases in the Pure Gas menu along with the ability to mix up to five gases using Gas-SelectX®. It also offers Calibration Validation with CAL-V™ to verify the meter is functioning correctly in the field.
Features include:

The Fox Thermal Model FT2A flow meter has a large selection of communication protocol options available intrinsically. Options include BACnet MS/TP, RS485 Modbus RTU, Profibus-DP, DeviceNet, or Ethernet Modbus TCP. NEMA 4X approved for hazardous locations.
Features include:
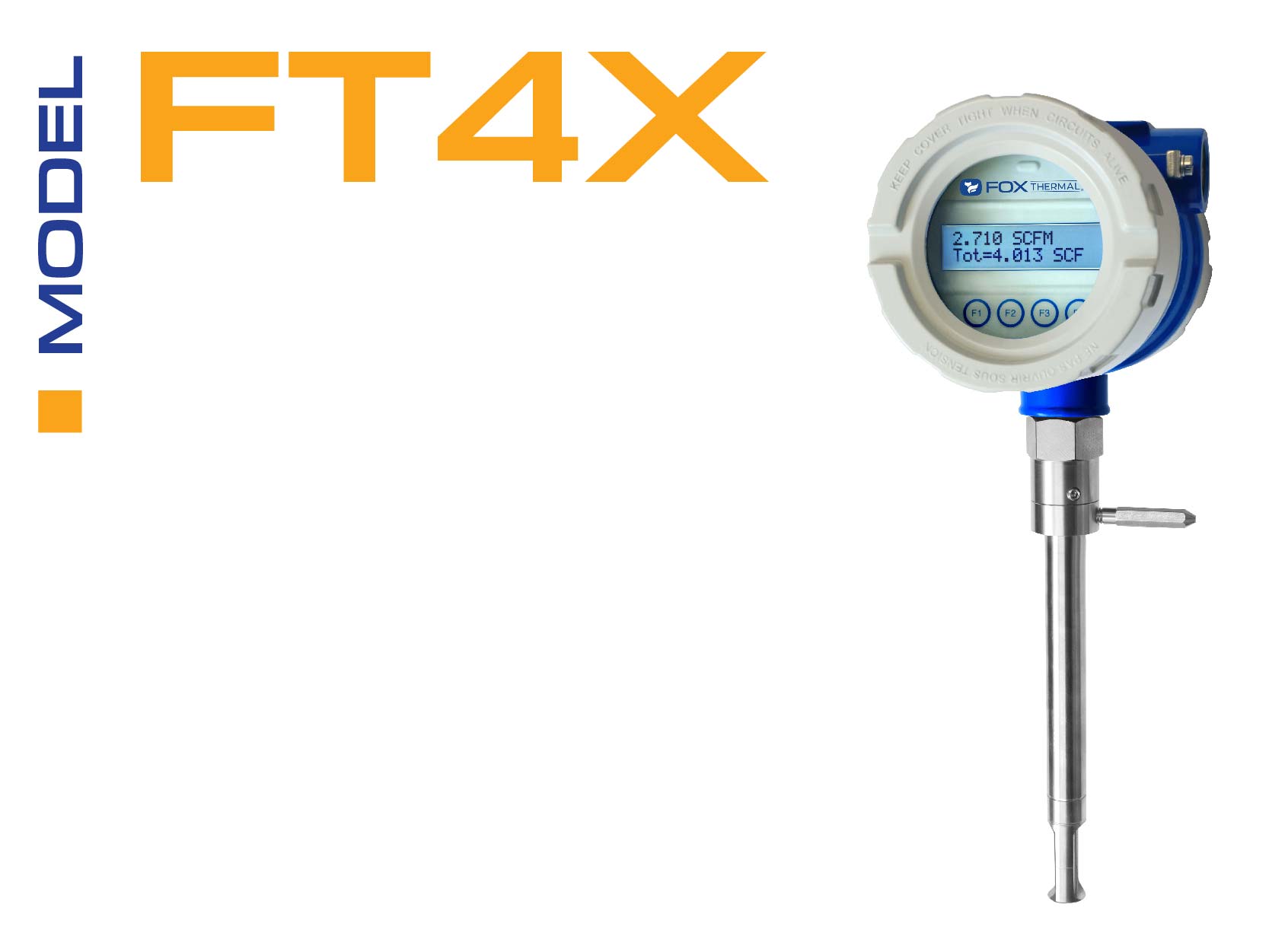

The Fox Thermal Model FT4X thermal gas mass flow meter comes with an advanced data logger which maintains a 7-year history for long-term record-keeping. This flow meter offers multiple configurations and an AC power input option.
Features include:
Properly managed, wastewater treatment reduces risks to the environment and public health caused by pathogens, toxic chemicals, antibiotics, and excess nutrients.
Gas flow measurements of compressed air in aerobic wastewater treatment can improve efficiency. For the anaerobic digestion of organic particles in wastewater, flow measurements can help keep track of biogas emissions. When biogas is used for heat or power generation, flow meters ensure accurate measurement of the fuel gas produced.
All of these operations in wastewater treatment plants require accurate measurement of gases flowing through the system.
An electromagnetic flow meter is not an option for measuring the flow of gases in wastewater applications, due to their low conductivity. Ultrasonic flow meters and Coriolis mass flow meters can be used, but these come at a higher cost than thermal mass flow meters.
The best flow meter technology for wastewater treatment facilities is thermal mass flow meters, which offer a low-cost, high-accuracy option with a wide turndown ratio.
For example, the Fox Thermal model FT4X thermal mass flow meter comes equipped with the state-of-the-art DDC-Sensor™ technology, new expanded Gas-SelectX® gas selection menu, CAL-V™ Calibration Validation, AC input power option, and a standard data logger with date and time stamp, for accurate emissions reporting.
Help Me Choose A Flow Meter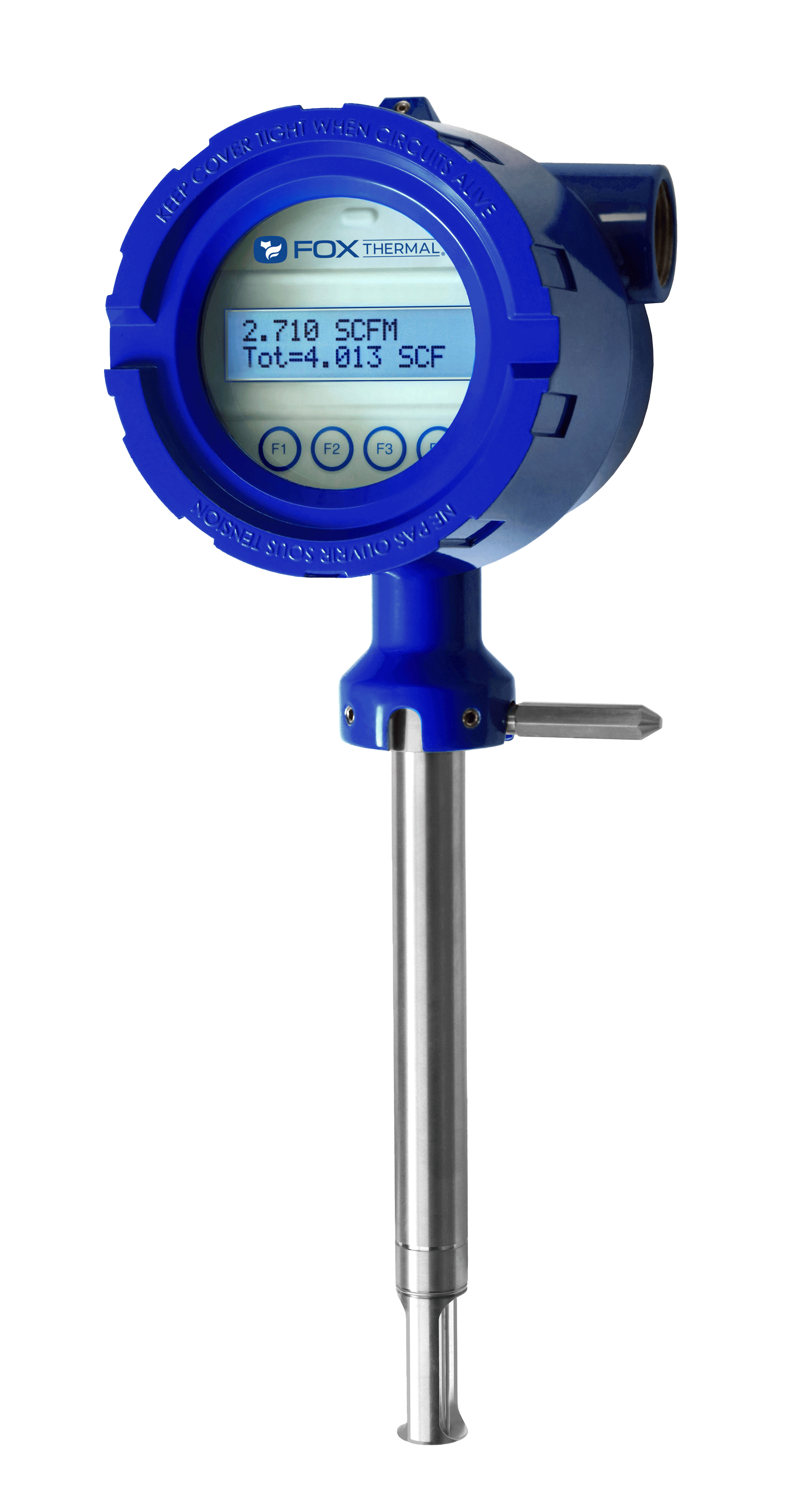
Wastewater treatment facilities play a crucial role in managing urban sanitation and safeguarding public health. However, these facilities also emit greenhouse gases, including methane (CH4), which contributes significantly to global warming. Cogeneration is a smart approach that not only addresses methane emissions but also harnesses them for energy production.
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, approximately 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) generate methane through the anaerobic decomposition of organic material during the treatment process.
One critical source of methane emissions in WWTPs is the sewage sludge, a byproduct of wastewater treatment. In plants equipped with digesters, the anaerobic breakdown of sludge produces biogas, which primarily consists of methane. Traditionally, this biogas was either flared (burned off) or released into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Instead of releasing or flaring the biogas, it is captured to fuel cogeneration equipment that powers the facility.
Monitoring biogas flow is essential to enhance efficiency and make the most of this sustainable solution. Thermal mass flow meters offer a cost-effective solution for monitoring the flow of biogas used in cogeneration at wastewater treatment facilities.
Talk to an Expert
If you're not sure which meter is right for your application, our Help Me Choose app walks you through a short series of questions to help you choose the ideal meter.
Next, enter your process data and flow meter requirements into our automated product configurator. Drop-down menus and Help icons will guide you to answer each question.
Save the data you entered into the configurator to create a PDF with a model code and AppID. When you're ready, submit your application to Fox Thermal for a quote.
To develop cleaner solutions for our global energy needs, new methods for producing hydrogen and combining it with natural gas will fuel the need for more accurate energy flow meters.
Choose the best technology for your wastewater application. Thermal mass flow meters are compared with differential pressure flow meters, turbine flow meters, Coriolis flow meters, ultrasonic flowmeters, and positive displacement flowmeters.
From pure hydrogen and hydrogen blend monitoring to fuel cells to natural gas transmission, Fox Thermal mass flow meters are the most accurate, reliable, convenient, and cost-efficient solutions on the market today.
Industrial gas flow meters must be rugged, packed with features and options, and ready to measure out of the box. Plant operators must often keep the process gas flow uninterrupted in order to keep production running.
Industrial gas mass flow meters by Fox Thermal provide easy installation with either insertion or inline style meters. This type of meter operates with no moving parts and offers a wide measurement range (up to 1,000:1, 100:1 typical).
View Industrial ApplicationsThe demand for natural gas has led to offshore exploration and horizontal fraction drilling. The flowback from shale oil plays has many different components that must undergo a process to separate the water/chemical solution from the oil and gas components.
Fox Thermal mass flow meters can accurately measure gas components for accounting and allocation purposes and can monitor exhaust and vent gases for environmental impact.
View Oil & Gas ApplicationsIndustrial customers of all types rely on specialty gas producers to supply them with the pure or mixed gases that they need for their processes. Thermal gas mass flow meters from Fox Thermal can help specialty gas producers and industrial process facilities maintain a leak-free system.
Whether used for transfer or submetering of gases such as nitrogen, argon, ethane, helium, and oxygen, thermal mass flow meters are a cost-effective and accurate solution for monitoring the flow of gases.
View Pure Gas ApplicationsFlow meters are increasingly being used to help companies meet the emissions criteria for the environmental goals their companies have established as part of their larger Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) programs. Thermal mass flow meters can be used to track gas consumption or emissions at facilities.
Fox Thermal customers use our flow meters to proactively monitor their gas emissions and log the data to achieve a positive ESG rating.
View ESG Applications